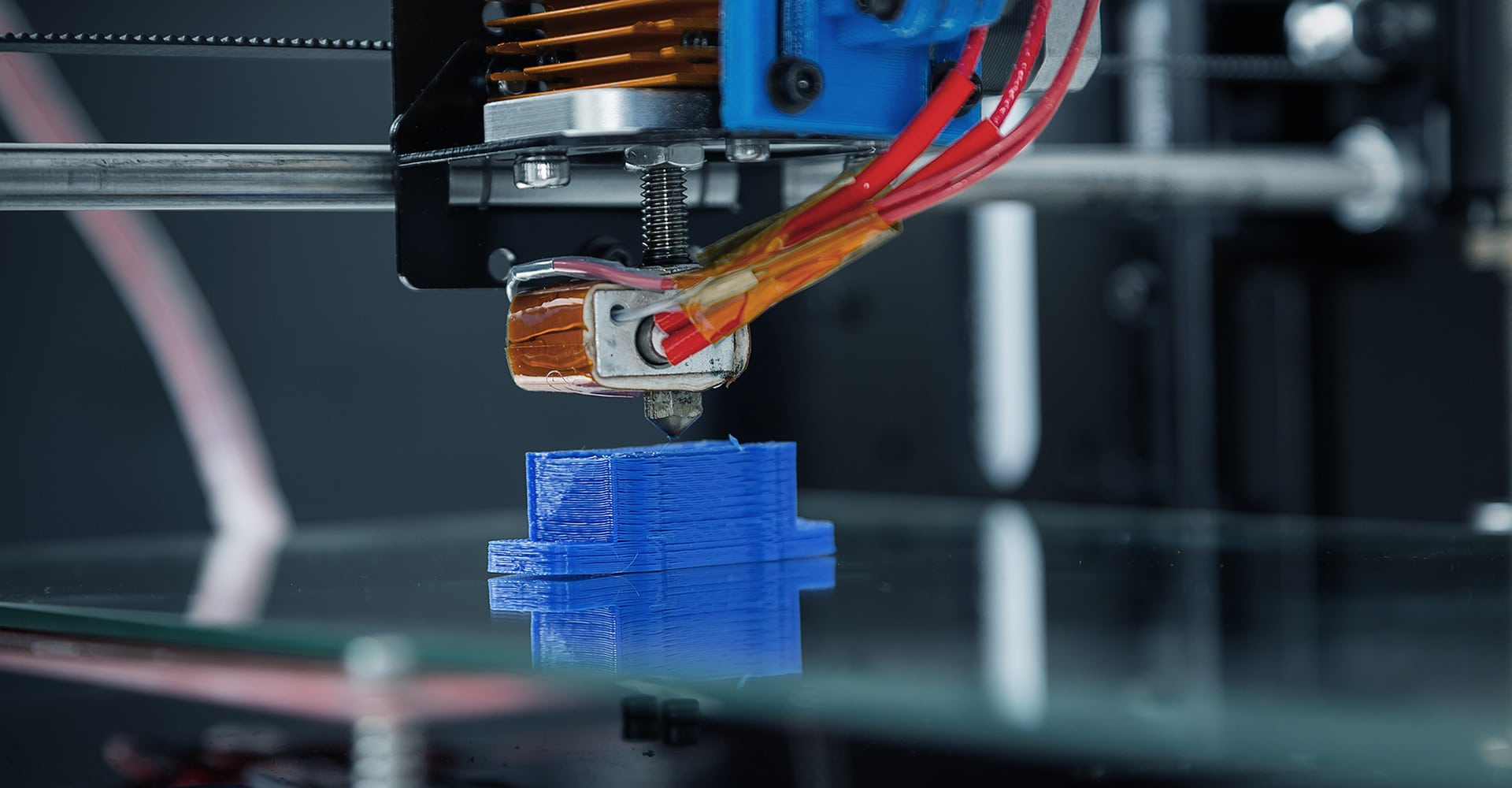
In the realm of mold manufacturing, selecting the right material can make all the difference in the quality, durability, and performance of the final product. Among the array of options available, Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PLA vs PETG) emerge as popular choices, each offering distinct advantages and applications. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the comparison between PLA and PETG to help you make an informed decision for your mold manufacturing needs.
Introduction to PLA and PETG
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a bio-based thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. It’s lauded for its eco-friendliness, ease of use, and minimal toxicity. PLA finds extensive usage in various industries, including mold manufacturing, owing to its biocompatibility and ability to produce intricate designs with high precision.
On the other hand, Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) is renowned for its exceptional strength, impact resistance, and transparency. Widely utilized across diverse sectors such as food packaging, medical devices, and consumer products, PETG stands out for its robust properties, making it an attractive choice for demanding mold manufacturing applications.
Properties and Characteristics
- PLA: PLA boasts biodegradability, low melting temperature, and ease of printing. It’s favored for its ability to yield smooth surface finishes and intricate details. However, PLA’s lower heat resistance limits its suitability for high-temperature applications.
- PETG: PETG shines with its outstanding mechanical properties, including high strength, impact resistance, and chemical stability. With a higher melting temperature compared to PLA, PETG is well-suited for molds exposed to elevated temperatures. It also excels in layer adhesion and dimensional stability, resulting in durable molds suitable for various applications.
Applications and Use Cases
- PLA: PLA finds its niche in mold manufacturing for prototyping, concept modeling, and low-temperature applications. Its biodegradable nature and ease of printing make it ideal for creating temporary or disposable molds, PLA vs PETG as well as for experimenting with new designs and concepts.
- PETG: PETG steps up to the plate for applications demanding durability, strength, and heat resistance. Commonly used in mold manufacturing for producing functional prototypes, production tools, and molds for injection molding, PETG delivers long-lasting performance in challenging manufacturing environments.
PLA and PETG
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic polymer derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It is known for its environmentally friendly properties, ease of use, and low toxicity. PLA is commonly used in 3D printing and mold manufacturing due to its biocompatibility and ability to produce intricate designs with high accuracy.
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) is a durable and versatile thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent strength, impact resistance, and transparency. PETG is widely used in various industries, including food packaging, medical devices, and consumer products. Its exceptional properties make it an attractive choice for mold manufacturing, especially for applications requiring toughness and durability.
Key Considerations in Material Selection
Several factors should be considered when choosing between PLA and PETG for mold manufacturing:
- Application Requirements: Assess the specific performance criteria, including temperature resistance, durability, and surface finish, required for your application.
- Printing Compatibility: Consider the printing capabilities of your 3D printer and the compatibility of the material with the printing process to ensure seamless production.
- Cost-effectiveness: Evaluate the overall cost-effectiveness of each material, factoring in material cost, waste generation, and production efficiency.
- Environmental Impact: Take into account the environmental implications of each material, considering factors such as biodegradability, recyclability, and sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between PLA and PETG for mold manufacturing hinges on the specific needs and requirements of your project. While PLA offers eco-friendliness and ease of printing, PETG delivers superior strength, durability, and heat resistance. By carefully considering the properties, applications, and key considerations outlined in this article, you can make an informed decision to select the best material for your mold manufacturing endeavors, ensuring optimal performance and success in your projects.