Common Types of Wrist Fractures and Effective Treatment Options
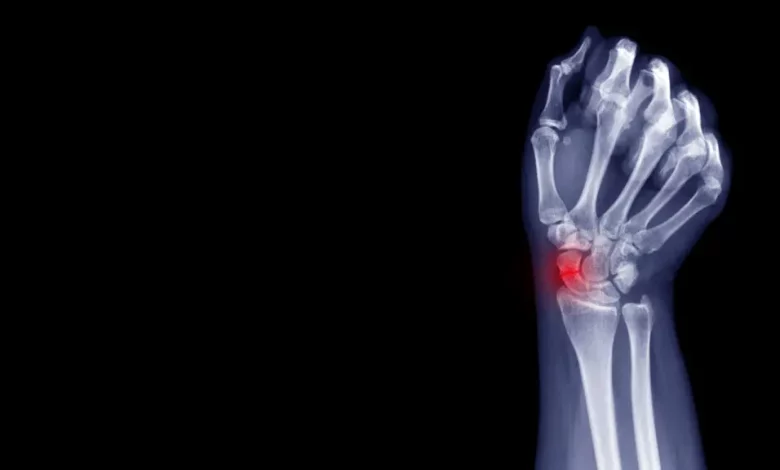
Wrist fractures are prevalent injuries due to various factors such as accidents, falls, sports-related incidents, or osteoporosis. These fractures can significantly impact an individual’s daily activities and require immediate medical attention. This post will explore common types of wrist fractures and the effective treatment options to promote healing and restore functionality.
Colles’ Fracture:
Colles’ fracture is one of the most common types of wrist fractures, typically caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand. It involves breaking the distal radius, the more prominent bone in the forearm that connects to the wrist. Treatment for Colles’ fracture may include:
- Immobilization: A splint or cast is initially applied to immobilize the wrist, allowing the bones to heal correctly. The immobilization duration depends on the fracture’s severity and the individual’s healing progress.
- Reduction: In some cases, if the fracture is displaced, a reduction procedure may be required to align the bones properly. This procedure involves manipulating the bones back into their correct position.
- Rehabilitation: Once the fracture has healed sufficiently, a rehabilitation program, including exercises and physical therapy, is often recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Scaphoid Fracture:
The scaphoid bone is located near the base of the thumb and is susceptible to fractures, often resulting from a fall on an outstretched hand. Due to its unique blood supply, scaphoid fractures may pose challenges in healing. Treatment options include :
- Immobilization: Similar to other wrist fractures, immobilization through a cast or splint is the initial step to allow proper healing. However, in the case of scaphoid fractures, immobilization is typically longer, ranging from several weeks to months.
- Surgery: In some instances where the fracture is displaced or fails to heal with conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery involves fixation of the fracture with pins, screws, or plates to promote proper alignment and stability.
- Rehabilitation: Following immobilization or surgery, a rehabilitation program is essential to restore wrist strength, stability, and range of motion. Occupational Therapy in Dallas, TX, exercises and a gradual return to normal activities are often prescribed.
Barton’s Fracture:
A Barton’s fracture occurs when the radius bone fractures at the wrist joint, affecting the articulation between the radius and the carpal bones. This type of fracture is usually the result of a high-energy injury or a forceful impact on the wrist. Treatment options for Barton’s fracture may include:
- Reduction and Fixation: In most cases, Barton’s fracture requires surgical intervention to realign the bones and stabilize the joint. The surgeon may use screws, plates, or wires to secure the fractured bones.
- Immobilization: Following surgery, the wrist is immobilized with a cast or splint to protect the repaired bones and allow them to heal correctly by consulting a Hand and Wrist Doctor in Dallas.
- Rehabilitation: After immobilization, a comprehensive rehabilitation program involving physical therapy is essential for regaining strength, improving flexibility, and restoring function to the wrist.
Conclusion:
Wrist fractures can significantly impact an individual’s daily life and functionality. Seeking prompt medical attention and receiving appropriate treatment is crucial for optimal recovery. The treatment approach for wrist fractures depends on the specific type and severity of the fracture and individual factors. Immobilization, reduction, surgical intervention, and rehabilitation programs are common strategies to promote healing, restore wrist function, and prevent long-term complications. If you suspect a wrist fracture, consult a Wrist Surgeon in Dallas for an accurate diagnosis & personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.