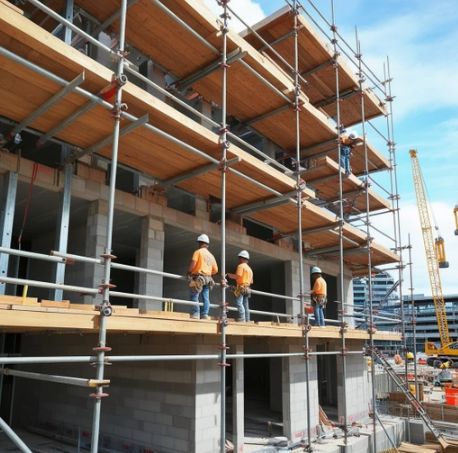
Scaffolding is a critical component in the construction and maintenance industries, providing workers with safe access to elevated work areas. However, to ensure safety, scaffolding must comply with stringent regulations. In Canada, these regulations are designed to minimize risks and protect workers from potential hazards associated with working at heights. This article explores the key scaffolding regulations in Canada and highlights their importance for businesses and workers alike.
Understanding Scaffolding Regulations in Canada
Scaffolding regulations in Canada are governed primarily by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety (CCOHS) and provincial occupational health and safety (OHS) authorities. These regulations address various aspects of scaffolding use, including design, construction, maintenance, and worker training. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory to ensure workplace safety and to avoid legal penalties.
Key Elements of Scaffolding Regulations
To understand the scaffolding regulations in Canada, it is essential to break them down into their primary components:
1. Design and Construction Standards
Scaffolding must be designed and constructed to meet specific standards outlined by the CSA Group (formerly the Canadian Standards Association). These standards ensure that scaffolding is strong, stable, and capable of supporting the intended load.
- Material Quality: Scaffolding materials, such as steel or aluminum, must meet high-quality standards to prevent structural failures.
- Load Capacity: The scaffolding must support at least four times the maximum intended load without risk of collapse.
- Guardrails and Toeboards: Guardrails, midrails, and toeboards are required to prevent workers and tools from falling.
2. Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspections are critical to ensuring the safety of scaffolding. Regulations require scaffolding to be inspected:
- Before Initial Use: A qualified professional must inspect scaffolding after it is erected to confirm compliance with safety standards.
- Daily or Before Each Shift: Inspections should identify any wear, damage, or structural issues.
- After Adverse Weather: Extreme weather conditions, such as strong winds or heavy rain, can compromise scaffolding stability and require reinspection.
3. Erection and Dismantling
Only trained and competent workers are permitted to erect or dismantle scaffolding. Regulations specify:
- Supervision: A qualified supervisor must oversee the erection and dismantling process.
- Stability: Scaffolding must be erected on a stable surface, with base plates or mud sills to distribute weight evenly.
- Secure Connections: All components must be securely fastened to prevent accidental disassembly.
4. Worker Training
Workers who use scaffolding must receive comprehensive training to understand:
- Hazard Identification: Recognizing risks such as falls, structural instability, and falling objects.
- Proper Use: Guidelines for safely climbing, working on, and descending scaffolding.
- Emergency Procedures: Steps to take in case of an accident or structural failure.
Provincial Variations in Scaffolding Regulations
While federal guidelines provide a baseline for scaffolding safety, each province and territory in Canada has its own specific regulations. Businesses must adhere to the rules in their respective regions. Below are examples of provincial scaffolding regulations:
Alberta
In Alberta, the Occupational Health and Safety Code outlines detailed scaffolding requirements. Key points include:
- Fall Protection: Workers must use fall protection systems when working at heights above 3 meters.
- Anchorage: Scaffolding must be securely anchored to prevent tipping.
- Access Points: Safe access, such as ladders or stairways, must be provided.
British Columbia
British Columbia’s WorkSafeBC regulations emphasize:
- Weather Considerations: Scaffolding must not be used in high winds unless secured.
- Scaffold Tags: Scaffolding must be tagged with inspection records to indicate its safety status.
Ontario
Ontario’s Construction Projects Regulation mandates:
- Height Restrictions: Scaffolding exceeding 15 meters in height requires specific design approvals.
- Worker Training: Mandatory working-at-heights training for all construction workers.
Businesses in Grande Prairie, Alberta, must pay special attention to local regulations and standards to ensure compliance. This is especially important for companies offering services like Scaffolding Grande Prairie, where safety is a top priority.
Common Hazards and How Regulations Mitigate Them
Scaffolding regulations are designed to address common hazards associated with working at heights. These hazards include:
1. Falls from Heights
Falls are the leading cause of workplace injuries and fatalities. Regulations require:
- Guardrails: To prevent accidental falls.
- Fall Arrest Systems: Harnesses and lanyards to protect workers.
2. Structural Failures
Improperly constructed scaffolding can collapse, leading to severe injuries. Inspections and load capacity standards mitigate this risk.
3. Falling Objects
Tools and materials falling from scaffolding pose risks to workers below. Toeboards and debris nets are mandatory to prevent such incidents.
4. Electrocution
Scaffolding erected near power lines can lead to electrocution. Regulations specify safe distances and grounding requirements.
The Importance of Compliance
Compliance with scaffolding regulations is not just a legal requirement but also a moral obligation to ensure worker safety. Non-compliance can result in:
- Fines and Penalties: Significant financial consequences for businesses.
- Workplace Accidents: Injuries or fatalities that harm workers and damage a company’s reputation.
- Project Delays: Accidents and inspections can halt construction projects, leading to costly delays.
Best Practices for Scaffolding Safety
To maintain compliance and promote safety, businesses should adopt the following best practices:
1. Regular Training
Provide workers with ongoing training to keep them informed about the latest safety protocols and regulations.
2. Detailed Inspections
Conduct thorough inspections at all stages of scaffolding use, from erection to dismantling.
3. Invest in Quality Equipment
Use high-quality scaffolding materials and components to ensure durability and reliability.
4. Engage Professionals
Hire qualified professionals for scaffolding design, erection, and inspection.
Conclusion
Scaffolding regulations in Canada are comprehensive and designed to prioritize worker safety. By adhering to these regulations, businesses can create a safer work environment, minimize risks, and avoid legal repercussions. For businesses in Alberta, especially those offering Scaffolding Grande Prairie, compliance with local and federal regulations is essential to ensure project success and worker well-being.
Prioritizing safety not only protects workers but also enhances a company’s reputation, making it a trusted name in the industry.