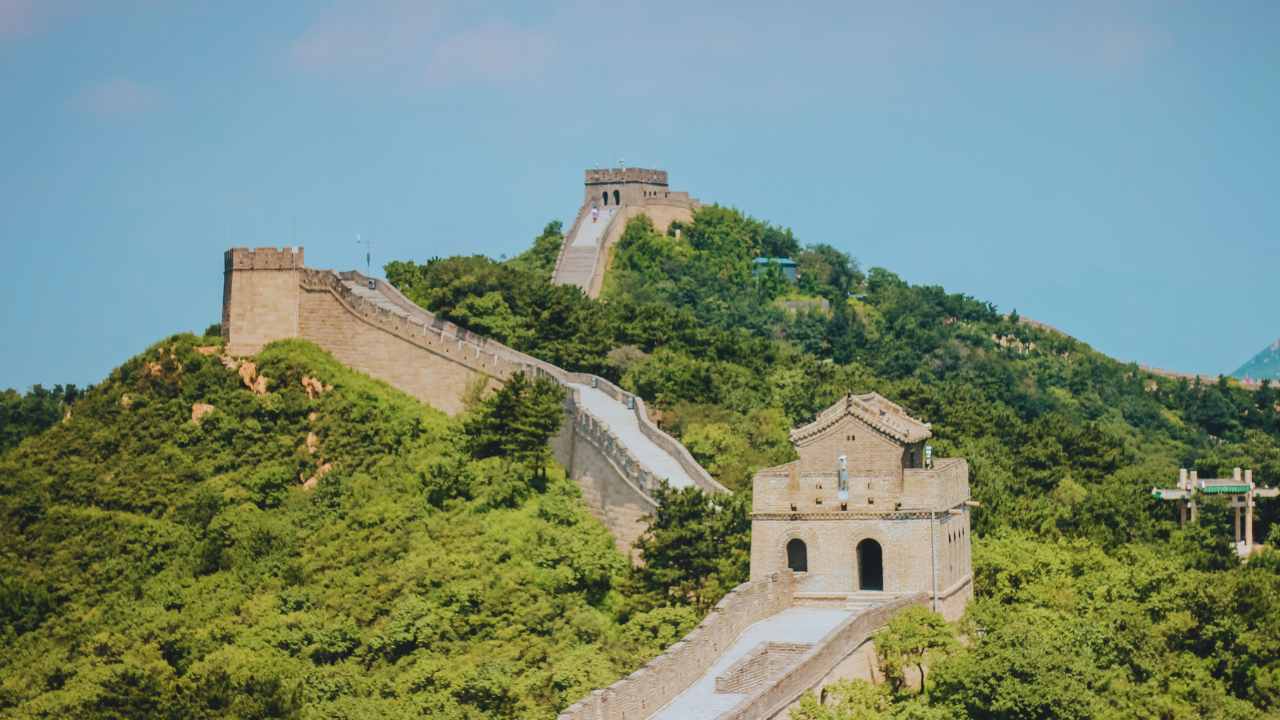
The Great Wall of China, an iconic symbol of Chinese civilization, has captivated the world with its grandeur and mystery for centuries. Spanning thousands of miles across northern China, this architectural marvel stands as a testament to human ingenuity and determination.
Historical Background
Warum ist die Chinesische Mauer wichtig? Construction of the Great Wall began over two millennia ago during the Qin Dynasty and continued through successive dynasties. Initially built for defense against nomadic invasions, it evolved into a symbol of imperial power and national identity.
Architectural Marvel
The Great Wall’s design varies, consisting of walls, watchtowers, and fortifications made from materials such as stone, brick, and rammed earth. Its impressive scale and intricate craftsmanship reflect the engineering prowess of ancient China.
Cultural and Symbolic Importance
Beyond its military function, the Great Wall embodies Chinese heritage and resilience. It symbolizes unity and strength, serving as a reminder of the nation’s ability to withstand external threats throughout history.
Tourism and Economic Impact
Today, the Great Wall attracts millions of visitors annually, contributing significantly to China’s tourism industry. Its popularity generates revenue for local communities and supports businesses in surrounding areas.
Conservation Efforts
Preserving the Great Wall poses challenges due to natural erosion and human activities. Conservation projects aim to protect its integrity while balancing the need for tourism and historical significance.
Myths and Legends
Numerous myths and legends surround the Great Wall, adding to its allure. From tales of supernatural guardians to stories of lost treasures, these narratives enrich the cultural tapestry of the landmark.
Modern Significance
In addition to its historical significance, the Great Wall plays a role in contemporary politics and diplomacy. It serves as a symbol of China’s global influence and its commitment to preserving cultural heritage.
Environmental Impact
Environmental factors such as erosion and pollution pose threats to the Great Wall’s longevity. Efforts to mitigate these risks include ecotourism initiatives and sustainable development practices.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology aid in the monitoring and maintenance of the Great Wall. Digital tools enable precise mapping and documentation, facilitating conservation efforts.
Educational Value
The Great Wall offers educational opportunities for visitors of all ages, fostering a deeper understanding of Chinese history and culture. Academic research conducted on-site contributes to scholarly discourse.
Future Prospects
Ensuring the Great Wall’s preservation for future generations requires sustainable strategies and international cooperation. Balancing conservation with tourism will be essential to safeguard its legacy.
Environmental Conservation Efforts
Preserving the Great Wall of China goes beyond structural maintenance. Conservation efforts focus on minimizing the environmental impact of tourism and natural erosion. Sustainable practices such as reforestation and erosion control help protect the surrounding ecosystem while maintaining the integrity of the wall.
Cultural Festivals and Events
Throughout the year, various cultural festivals and events celebrate the Great Wall’s rich history and significance. These festivities attract both locals and tourists, offering opportunities to immerse oneself in traditional music, dance, and cuisine. Such events foster a deeper appreciation for the cultural heritage embodied by the Great Wall.
Educational Programs for Youth
Educational programs aimed at schoolchildren play a vital role in transmitting the legacy of the Great Wall to future generations. Field trips and interactive workshops provide hands-on learning experiences, allowing students to explore the wall’s historical significance and architectural marvels. By engaging youth in the preservation and appreciation of the Great Wall, these programs ensure its enduring relevance for years to come.
Comparison with Other Wonders
Comparing the Great Wall to other historical wonders highlights its unique features and enduring significance. Each landmark tells a story of human achievement and resilience in the face of adversity.
Personal Reflections
Visitors to the Great Wall often describe it as a humbling and awe-inspiring experience. Their testimonials convey the profound impact of encountering this iconic symbol of human endeavor.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Great Wall of China stands not only as a physical barrier but as a cultural treasure and symbol of resilience. Its significance transcends time and borders, inspiring admiration and wonder around the world.